Diseases Wellness Rise Rraft

changes in the position of your teeth or loose teeth. receding gums. red, tender, or swollen gums. buildup of plaque or tartar on your teeth. pain when chewing. tooth loss. foul taste in your.
How Long Can Periodontal Disease Keep Your Teeth?

As long as patients maintain periodontal health through regular maintenance and care, they may keep their natural teeth for many years, or even lifetime. However, some patients suffer from aggressive or advanced periodontal disease that progresses despite standard treatments.
How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth With Periodontal Disease?

Teeth with Periodontitis. Periodontitis is a more advanced stage of periodontal disease. It occurs when gingivitis goes untreated and infection sets in. It can cause tooth loss, painful chewing, further separation of gums from teeth, bleeding gums, and other health problems. Eventually, periodontitis can break down the gums, connective tissues.
Periodontal Disease Stages of Periodontal Disease Before and After

At this advanced point of periodontal disease, tooth loss, bone deterioration, and widespread infection become inevitable. A compromised immune system weakens your ability to fend off infection, heightening major health risks like diabetes and heart disease. How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth with Advanced Periodontal Disease?
Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease) Treatment Sound Dental

The good news is that gingivitis is reversible with proper oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings. Periodontal disease, also known as periodontitis, is a more advanced stage of gum disease that occurs when gingivitis is left untreated. In periodontitis, the inflammation extends from the gums to the bone and supporting structures of the teeth.
How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth With Periodontal Disease?

With gum disease, you won't keep your teeth for long. In fact, unlike tooth decay which impacts your smile one tooth at a time, periodontitis can cause you to lose multiple, if not all, teeth at once. Gum disease starts small as a mild form called gingivitis. Gingivitis is painless in most cases, though you may treat it at home with a.
There are some hard to reach places around your teeth. Dental sealants can help to keep your

Early Periodontal disease, or Periodontitis, will begin after a case of untreated gingivitis in a few weeks. Plaque buildup around teeth and gums will start to harden and become tartar. A dentist will diagnose you with early gum disease if there is a 4-5mm gap between your gums and teeth. Tartar + Bacteria = Receding Gums and Teeth.
Periodontal (Gum) Disease Institute of Dental Implants & Periodontics
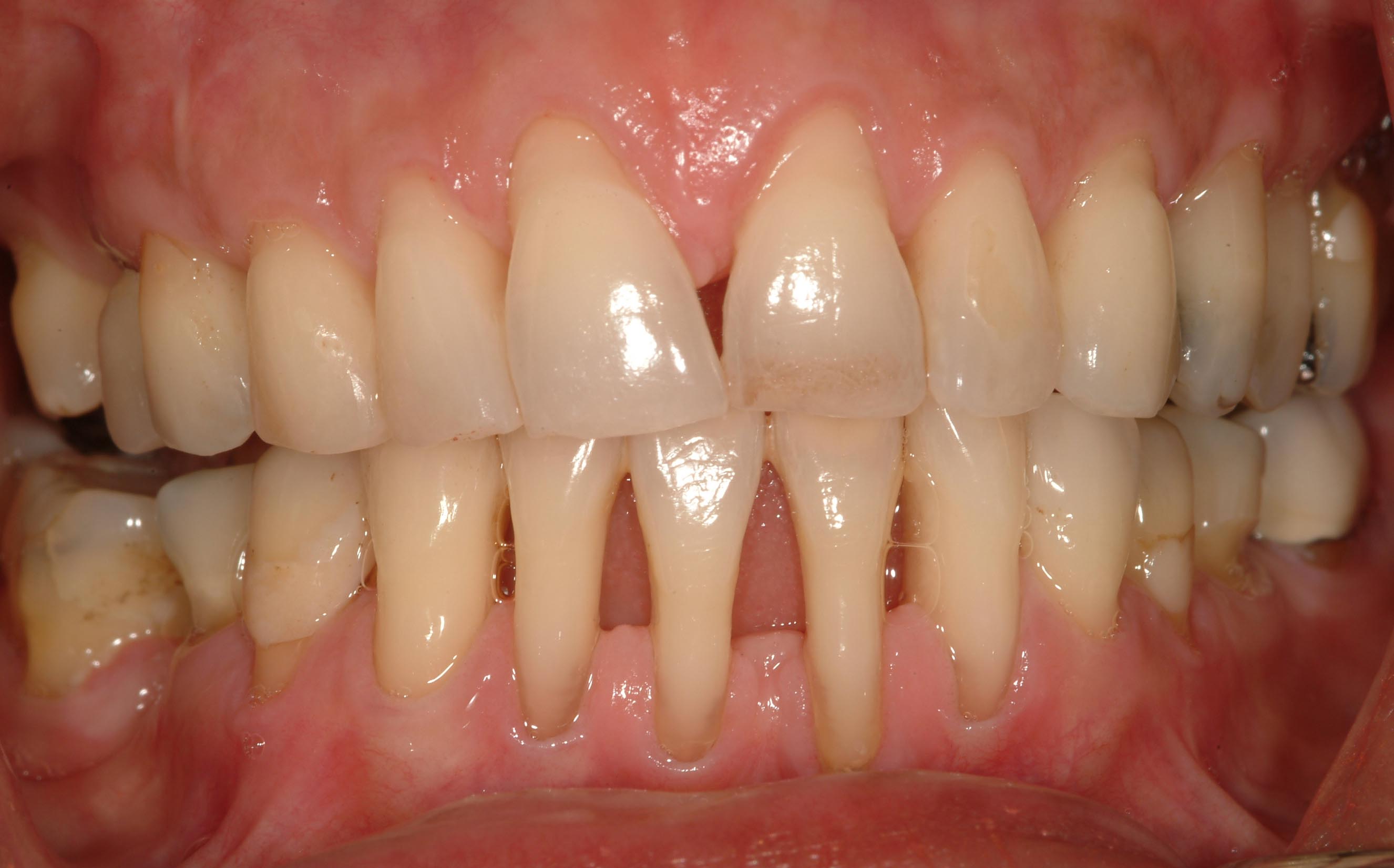
Defining Periodontal Disease. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, involves inflammation and infection of the tissues that support your teeth. It starts when bacteria build up on teeth, forming plaque. If not removed, plaque turns into tartar, leading to gingivitis - which is first stage periodontal disease.
How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth With Periodontal Disease Droitwich Dental Studio

It's a team effort to keep your teeth in tip-top shape! Preserving Your Teeth with Periodontal Disease. You're in this for the long haul, my friend! By taking action and sticking to your treatment plan, you can preserve your teeth like a champ: Keep good oral hygiene: Brush 'em at least twice a day with a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride.
How long can you keep your Teeth with Periodontal Disease?
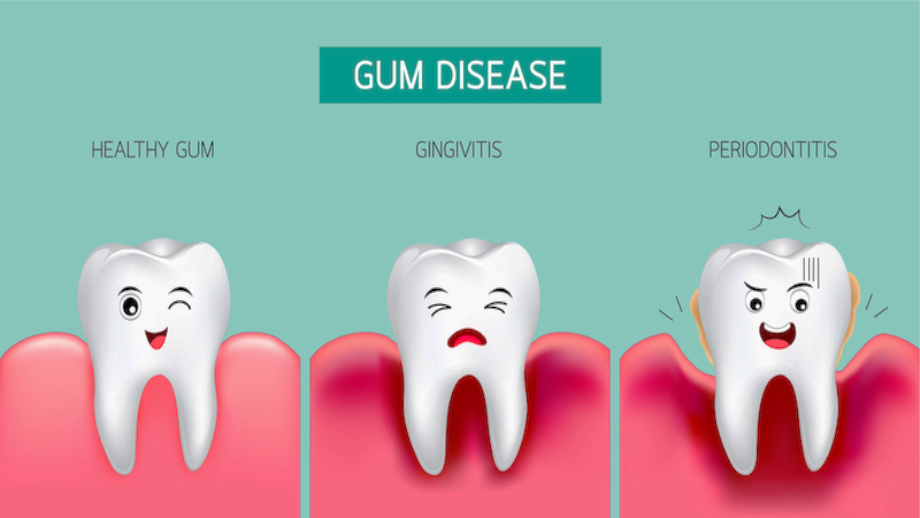
Periodontal disease is inflammation and infection of your gums and the bone that supports your teeth. It can be a result of poor hygiene, but some people are more prone to this type of infection. Symptoms may include bad breath, loose teeth and bleeding, swollen gums. There are many treatments available, depending on the severity of disease.
How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth With Periodontal Disease Droitwich Dental Studio

By addressing these factors head-on and adopting a comprehensive oral care routine, you can slow down the progression of the disease, giving your teeth a better chance at long-term survival. Beyond the immediate impact on your teeth, untreated periodontal disease has been linked to systemic health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and.
How Long Can You Keep Your Teeth with Periodontal Disease?

Periodontitis Enlarge image. Periodontitis (per-e-o-don-TIE-tis), also called gum disease, is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue around teeth. Without treatment, periodontitis can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. This can cause teeth to loosen or lead to tooth loss. Periodontitis is common but can usually be prevented.
Bleeding Gum Dentist 3 Stages of Periodontal Disease Know The Signs
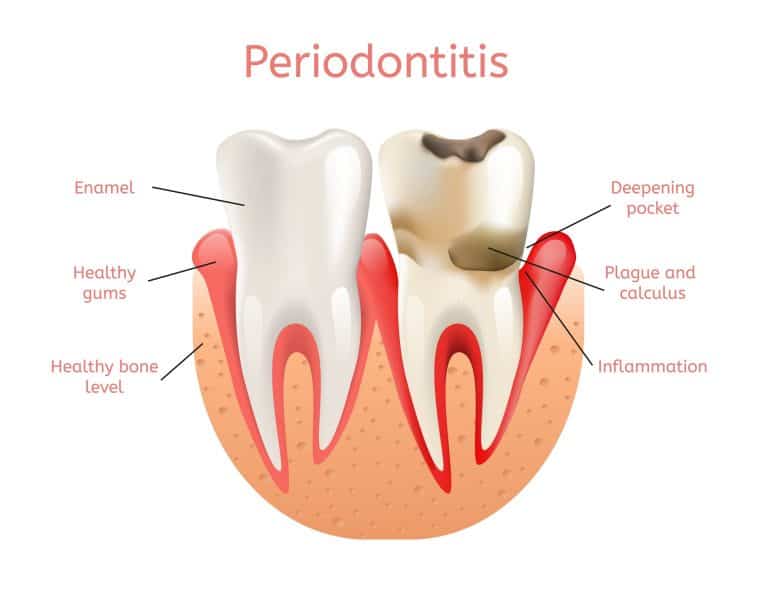
Posted February 2, 2024 in Periodontal Disease. Advanced periodontal disease threatens the health of your mouth, teeth, and gums. If left untreated, it can cause the loss of multiple teeth. The earlier patients catch periodontitis, the more options they have for treatment and the ability to preserve their natural teeth.
How Long Can You Keep Your teeth With Periodontal Disease?
Let's look at the treatment options for each stage of gum disease. 1. Treatment for Gingivitis. The purpose of Dr. Harald Löe's experiment (though this type of research is considered unethical in today's research guidelines) was to prove that the mildest form of gum disease, gingivitis, is completely reversible.
Gum Disease Periodontal Disease Lakeview Family Dentists

They can spread and cause bleeding when you brush. Bleeding gums are often the first sign of gum disease. If the plaque buildup continues to worsen, the bleeding usually gets worse. The reality is that your gums shouldn't bleed when you brush and floss. Your gums may also swell, turn red, or become sore.
Hygiene Visits During Orthodontics Schur Orthodontics

Out of 2139 teeth from the 600 people studied, 666 were lost. In summary, about 31% of the teeth in people with periodontal disease were lost in a 22 year examination period, with half of all participants having no teeth lost at all! In another study in 2003, tooth loss was examined across a 12 year time span for 156 patients, and only 61.